Moisture Measurement
What is Moisture Measurement?
Moisture measurement determines the water content of a material.
Moisture measurement is often misunderstood and deemed unreliable; It has often been said that “moisture measurement doesn’t work!”.
There are numerous moisture measurement techniques and some work better than others in different applications and materials. It is important to choose the appropriate sensor, designed specifically for use in an application and material in order to achieve positive results.
Benefits of moisture measurement
Automate your process
- Reduce waste
- Use your equipment effectively
- Remove the need to perform regular offline sampling
- Enable staff to focus on their day job
“The installation of a moisture sensor in our parboiled rice production has enabled us to reduce the amount of wasted rice by 2.5% which equates to 4 tonnes per week. An annual saving of 192 tonnes for 48 weeks.”
Start your sustainability journey
- Reduce your spoiled material
- Cut your CO2 emissions
- Start your journey towards net zero
Reduce the moisture variation in mixed concrete to +/- 0.1% to enable savings of 29kg of cement per cubic metre of the concrete being produced which is equivalent to saving 20kg CO2e/m3 .
Increase your yield/profitability
- Ensure you produce a consistent final product to the standard desired
- Easily adjust to change in the raw materials
By reducing the amount of over-drying, you can gain 0.5% weight of finished product. If you’re drying 1000 tonnes per hour, you’re gaining hourly an extra 5 tonnes of material.
Improve the quality of your final product
- Ensure you produce a consistent final product to the standard desired
- Easily adjust to change in the raw materials
A UK brick manufacturing plant implemented a moisture control system which allowed them to increase production and reduce waste:
- increased production uptime by 9.2%
- 80% reduction in material waste
- increased annual brick production by 5 million units
Increase your return on investment
- Increase production levels
- Improve your processes
- Save costs (energy, waste)
Batch Plant example:
- 2m³ mixer
- 10 batches per hour
- 2x shifts with 5 hrs per shift
- 200m³ concrete production per day
Saving 30kg of cement/m³
- 6000kg of Cement per day
- Saving per day = £300
(Based upon cost of cement = £75/tonne)
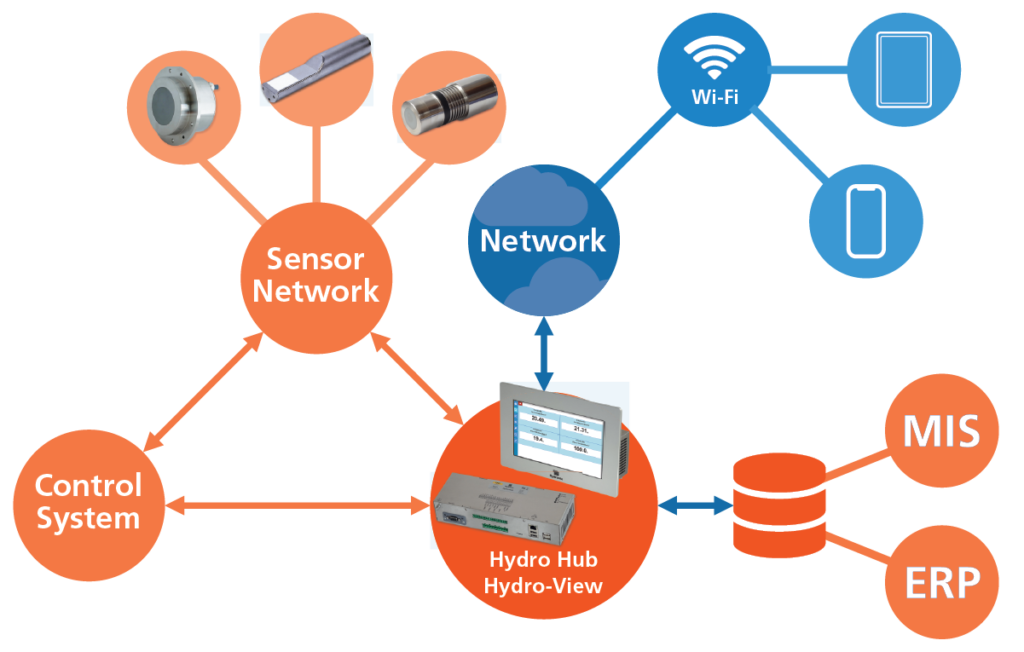
Collect sensor data
- Collect data from various plants and sites
- Analyse moisture data to improve your processes and overall performance

How is moisture content calculated?
The moisture content is often calculated as a percentage and typically uses two methods: wet basis or dry basis.
- Wet basis, typically used in agricultural and food processing industries: the amount of water divided by the total weight of the material, including the water.
- Dry basis, typically used in the construction industry and drying applications: the water content divided by the dry weight of the material, in this case excluding the water.
Why do we need to measure moisture?
Moisture or water is found naturally in many materials and controlling the moisture content is critical to many processes such as concrete production, oil extraction, animal feed production to name but a few. It is important to measure moisture for many reasons. Some include:
- Efficient use of materials – maintaining the material/water ratio
- Blend materials – obtain the correct proportion of dry materials in the mix
- Optimise processes – many processes work best at particular moisture contents
- Reduce wear on processing machinery
- Reduce wastage caused by incorrect moisture content
- Ensuring the correct consistency of the material
What are the different methods to measure moisture?
Most processes require real time monitoring and adjustment of moisture if the incoming material moisture content varies. Moisture sensors are installed on the process line and are able to measure the moisture of the material continuously.
Sensors using Infra-Red, Resistance, Capacitance, Nuclear, and Microwave measurement techniques exist. Understanding which technique to use to obtain the best results in a specific process is vital.
Microwave and NIR. Complementary, not competitive, technologies
There is a common misconception that, where moisture measurement is required, there is a choice between NIR and microwave sensors. Both technologies can measure moisture, but each has its advantages…
Read more
The benefits of online measurement over offline laboratory tests
Moisture is a constantly varying component in the raw materials for many industrial applications and it is becoming more critical to measure and control accurately. Often laboratory tests are seen…
Read moreWhat makes Hydronix technology unique?
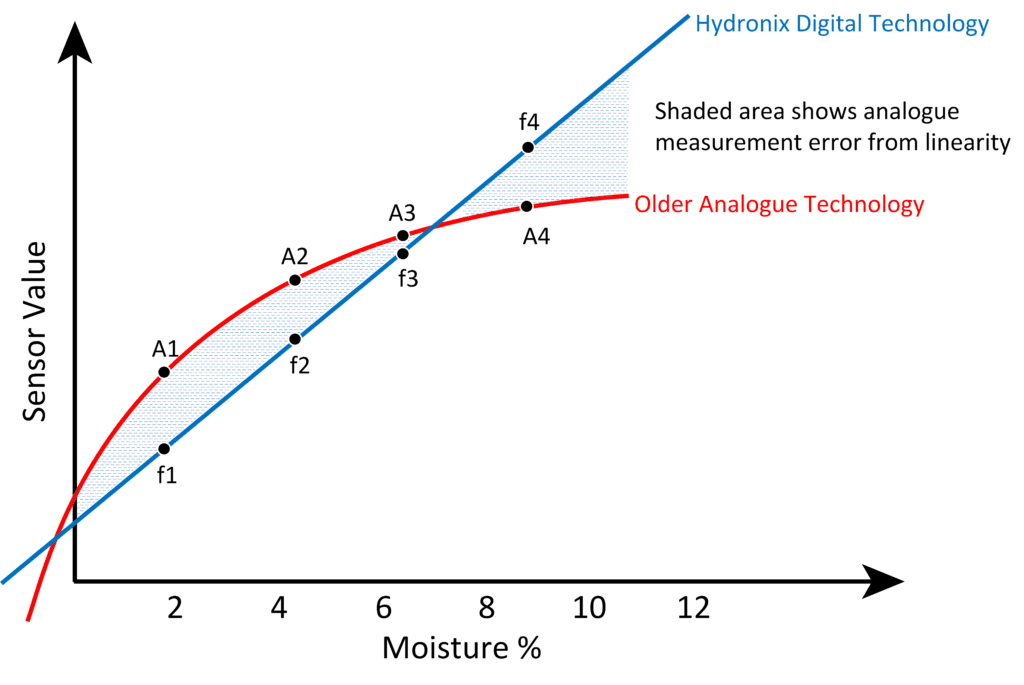
The Hydronix sensor utilises a unique measurement technique to determine the number of water molecules present in the material.

The sensor value has a linear relationship with the moisture content of a material. This is simple to calibrate by collecting samples from the process whilst in production.
Latest News, Blogs & Events
Latest News & Blogs

